How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in many, from hobbyists captivated by aerial photography to professionals exploring diverse applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, providing a structured approach to understanding its components, mastering flight techniques, and adhering to safety regulations. From pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource for learning the basics is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide will help you safely and effectively control your drone, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive flying experience.
Safe and responsible operation is paramount when learning how to operate a drone.
We’ll explore the fundamental mechanics of drone flight, examining everything from the individual parts and their functions to the crucial pre-flight preparations that ensure safe and successful operation. The guide then progresses to practical flight instructions, covering both basic and advanced maneuvers, emphasizing safe and responsible flying practices. Finally, we’ll address the important aspects of drone maintenance, legal considerations, and the various applications of this remarkable technology.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the function of key components and explores the differences between various types of motors and propellers.
Drone Component Functions
A typical drone comprises several key components. The propellers generate thrust, powered by electric motors controlled by the flight controller. The battery provides the power for the entire system, while the GPS module aids in navigation and autonomous flight. The camera captures images and videos, and the radio transmitter and receiver enable communication between the pilot and the drone.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the lift and thrust necessary for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to spin the propellers. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the “brain” of the drone, processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the pilot.
- Battery: Provides power to all drone components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are standard, offering high energy density.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation, crucial for autonomous flight modes and features like “Return to Home”.
- Camera: Captures images and videos. Different drones offer various camera resolutions, features, and image stabilization capabilities.
- Radio Transmitter and Receiver: Allow the pilot to control the drone wirelessly. The transmitter sends signals, and the receiver on the drone interprets them.
Motor and Propeller Types
Drone motors are primarily brushless DC motors, known for their efficiency and long lifespan. Propellers vary in size, pitch, and material. Larger propellers generally provide more thrust, while pitch affects the speed and efficiency of the lift generated. Different materials offer varying levels of durability and weight.
Common Drone Battery Specifications, How to operate a drone
Battery selection significantly impacts flight time and drone performance. The following table compares specifications of common drone batteries:
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | 1500 | 11.1 | 20-25 |
| Example 2 | 2200 | 14.8 | 30-35 |
| Example 3 | 3000 | 14.8 | 40-45 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, calibrating sensors, and ensuring the surrounding environment is suitable for flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Visually inspect the drone for any damage to propellers, motors, or other components.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify that all propellers are securely attached.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a proper connection.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensors.
- Check GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Review the surrounding environment for obstacles and potential hazards.
- Ensure you have sufficient space and clear airspace for the planned flight.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Accurate compass and sensor calibration are crucial for stable and controlled flight. Incorrect calibration can lead to erratic behavior and potential crashes. Most drones have built-in calibration procedures accessible through their control apps.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process aids in ensuring all necessary steps are followed consistently. (Note: A flowchart would be visually represented here, but text-based description is provided instead.) The flowchart would start with “Power on Drone and Controller,” then branch to “Visual Inspection,” “Battery Check,” “Propeller Check,” “Sensor Calibration,” “GPS Check,” “Environment Check,” and finally “Flight Ready”.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe drone operation. This section explains the functions of the control sticks and provides tips for maintaining stable flight and avoiding crashes. Mastering these fundamentals is crucial before attempting more advanced maneuvers.
Control Stick Functions
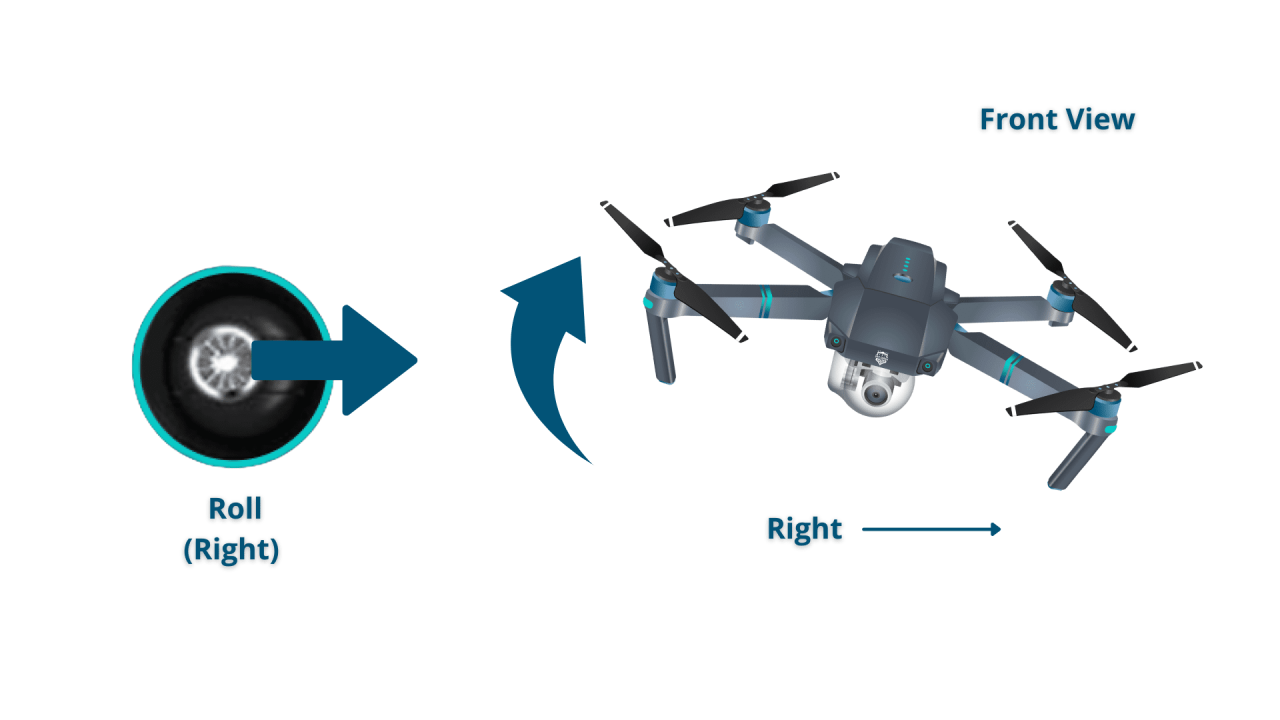
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks. One controls the throttle (altitude) and pitch (forward/backward movement), while the other controls roll (left/right movement) and yaw (rotation). Understanding how these controls interact is key to smooth and controlled flight.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Pushing up increases altitude, pushing down decreases it.
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement. Pushing forward moves the drone forward, pushing backward moves it backward.
- Roll: Controls left and right movement. Pushing right moves the drone right, pushing left moves it left.
- Yaw: Controls rotation. Pushing right rotates the drone clockwise, pushing left rotates it counter-clockwise.
Maintaining Stable Flight

Smooth and precise control stick movements are essential for stable flight. Avoid abrupt movements, especially when hovering or at low altitudes. Practice in a safe, open area to develop good control habits.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering hovering, ascending, descending, and turning are essential for basic drone operation. Practice each maneuver individually before combining them for more complex flight patterns. Start slowly and gradually increase speed and complexity as your skills improve.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight, pilots can explore advanced techniques utilizing GPS and autonomous flight modes. However, these maneuvers require extra caution and awareness of potential challenges and safety considerations.
GPS and Autonomous Flight Modes
GPS enables features like “Return to Home” (RTH), waypoint navigation, and automated flight paths. These modes enhance flight capabilities but require careful planning and consideration of potential GPS signal interference.
Challenges and Safety Considerations
Advanced maneuvers, such as high-speed flights or close-proximity operations, increase the risk of accidents. Always maintain visual contact with the drone, be aware of wind conditions, and practice in a safe, controlled environment.
Best Practices for Various Weather Conditions
Weather significantly impacts drone flight. Strong winds can make control difficult, while rain or snow can damage the drone’s electronics. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions. If flying in windy conditions, use appropriate flight settings and maintain extra caution.
- Low Wind: Ideal conditions for most flights.
- Moderate Wind: Requires more precise control and potentially reduced flight speed.
- High Wind: Avoid flying in high winds due to significant risk of loss of control.
- Rain/Snow: Avoid flying in wet conditions to prevent damage to electronics.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Many drones are equipped with high-quality cameras capable of capturing stunning photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for maximizing image quality.
Camera Settings and Functions
Drone cameras typically offer adjustable settings like resolution, ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. Understanding how these settings interact is crucial for capturing high-quality images and videos in various lighting conditions.
- Resolution: Determines the image size and detail. Higher resolutions result in larger files but better image quality.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-number) allows more light, useful in low-light conditions, but can reduce depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Optimal camera settings depend on the lighting conditions and desired effect. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your specific needs. Consider using image stabilization features to reduce camera shake.
Optimal Camera Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
| Lighting Condition | Resolution | ISO | Shutter Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Sunlight | 4K | 100 | 1/500s |
| Overcast | 4K | 200 | 1/250s |
| Low Light | 1080p | 800 | 1/60s |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your drone and prevents potential malfunctions. This section details a routine maintenance schedule and provides troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Inspect your drone after each flight for any damage or debris. Clean the propellers and body regularly. Store the drone in a cool, dry place to protect the battery and electronics.
- After Each Flight: Inspect for damage, clean propellers and body.
- Weekly: Check battery health, inspect connections.
- Monthly: More thorough inspection of all components, clean sensors.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common issues include low battery, motor malfunctions, GPS signal loss, and communication problems. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps. If problems persist, seek professional assistance.
Extending Drone Battery Lifespan
Proper battery care is crucial for maximizing its lifespan. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging the battery. Store batteries in a cool, dry place when not in use.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices

Adhering to local drone regulations and safe flying practices is paramount for responsible drone operation. This section emphasizes the importance of safety and provides guidelines for responsible use.
Importance of Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to understand and comply with all applicable laws and regulations before flying. This may include registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Safe Flying Practices to Avoid Accidents and Injuries
Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone. Avoid flying near people, buildings, or other obstacles. Be mindful of wind conditions and weather patterns.
Safety Guidelines for Responsible Drone Operation
- Register your drone if required by local regulations.
- Always maintain visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Be aware of wind conditions and weather patterns.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid disturbing others.
Drone Software and Apps: How To Operate A Drone
Drone control apps and software play a vital role in drone operation, providing access to various features and settings. This section explores different applications and their functionalities.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and responsible flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Once you’ve grasped the fundamentals, you’ll be ready to explore the exciting possibilities of aerial photography and videography with your drone.
Comparison of Drone Control Apps
Many apps offer features such as flight control, camera settings, GPS navigation, and autonomous flight modes. The specific features available depend on the drone model and the app’s capabilities. Some popular apps include [List of examples, mentioning key features of each].
Updating Drone Firmware and Software
Regularly updating your drone’s firmware and software ensures optimal performance and access to new features. Check your drone manufacturer’s website for the latest updates and instructions.
Guide for Using Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows for pre-programming flight paths and waypoints, useful for complex aerial photography or surveying tasks. This software often integrates with drone control apps, streamlining the flight planning process. Examples include [List of examples and brief description of their functionalities].
Illustrative Examples of Drone Usage
Drones find applications across various industries. This section illustrates their versatility through real-world examples.
Drone Applications in Different Industries
Drones are used extensively in photography and videography, agriculture (crop monitoring, spraying), infrastructure inspection, search and rescue operations, and delivery services.
Detailed Scenario: Search and Rescue Operation
In a remote mountainous region, a hiker is reported missing. A drone equipped with a thermal camera is deployed to search the area. The drone’s high-altitude vantage point and thermal imaging capabilities allow rescuers to quickly locate the missing hiker, even in challenging terrain and low-light conditions. The drone’s live video feed provides real-time information to the rescue team, guiding them to the hiker’s location, significantly reducing search time and increasing the chances of a successful rescue.
The drone’s maneuverability allows it to navigate around obstacles and cover a large area efficiently.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of learning and practice. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the technical aspects, flight procedures, and safety regulations involved. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to safety guidelines, and a continuous pursuit of knowledge are crucial for becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the exciting world of aerial exploration while prioritizing safety and responsible operation.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functionality, and intuitive control apps.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery capacity, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) feature that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Check your local laws and regulations before flying. In many places, registration and licensing may be required for certain drone types or operations.
